The human body is a complex and fascinating structure, made up of various parts that function together to support life. Understanding the name body parts and their functions are essential not only for medical professionals but also for general knowledge and education. Let’s explore the different regions of the body and the parts they encompass.
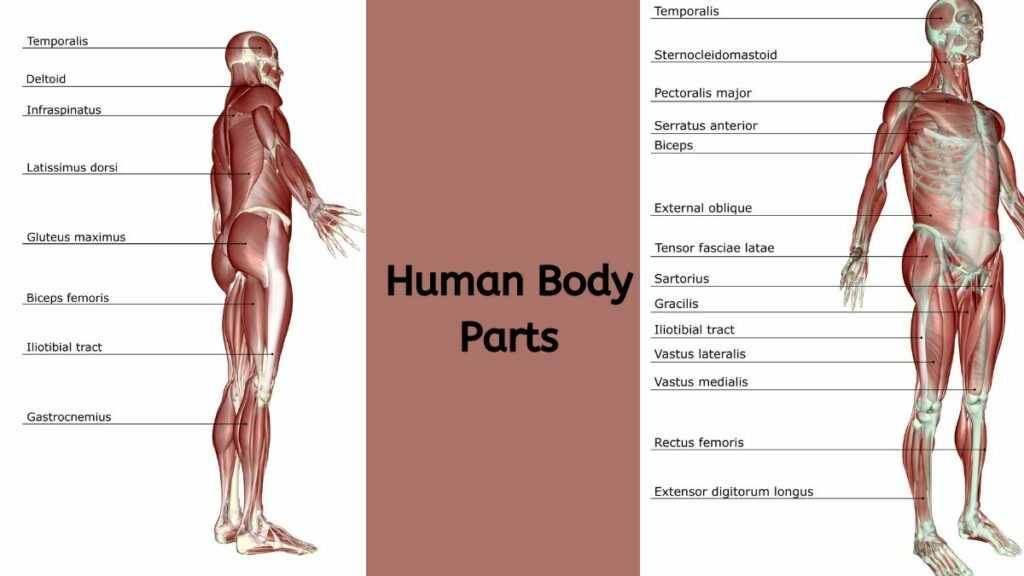
Head and Neck
The head and neck region is a complex structure that houses vital sensory organs and pathways:
- Skull: Encases and protects the brain, made up of several bones.
- Brain: The body’s control center, responsible for thought, emotion, and coordination.
- Eyes: Enable vision, each eye containing parts like the retina, iris, and cornea.
- Ears: Facilitate hearing and balance, including the outer, middle, and inner ear.
- Nose: Involved in smell and breathing, made up of nostrils, nasal cavity, and sinuses.
- Mouth: Used for eating, speaking, and breathing, includes teeth, tongue, and salivary glands.
- Throat: Comprises the pharynx and larynx, essential for swallowing, breathing, and voice production.
- Neck: Supports the head, contains the cervical spine, muscles, and thyroid gland.
Upper Body
The upper body consists of various parts that enable movement and protect vital organs:
- Shoulders: Complex joints that connect the arms to the torso, allowing a wide range of motion.
- Arms: Comprised of the upper arm, forearm, wrist, and hand, including bones like the humerus, radius, and ulna.
- Hands: Essential for grasping, made up of fingers, thumbs, and numerous small bones and joints.
- Chest: Houses the heart and lungs, protected by the ribcage, sternum, and associated muscles.
- Back: Includes the spine, which supports the body and protects the spinal cord, made up of vertebrae, discs, and various muscles.
Midsection
The midsection is a central region containing vital digestive and metabolic organs:
- Stomach: Part of the digestive system, breaks down food with enzymes and acids.
- Liver: Largest internal organ, essential for metabolism, detoxification, and storage of nutrients.
- Kidneys: Bean-shaped organs that filter blood, remove waste, and regulate electrolytes.
- Intestines: Include the small and large intestines, responsible for nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
- Pancreas: Dual-function organ that produces digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin.
- Spleen: Part of the immune system, filters blood and helps fight infections.
- Gallbladder: Stores bile, aiding in fat digestion.
Lower Body
The lower body includes the legs and feet, essential for support and mobility:
- Hips: Ball-and-socket joints that connect the legs to the torso, allowing movement in multiple directions.
- Thighs: The upper part of the legs, containing the femur, the largest bone in the body.
- Knees: Complex joints that allow bending and straightening of the legs, made up of ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
- Legs: Include the shins and calves, made up of bones like the tibia and fibula.
- Ankles: Joints that connect the legs to the feet, allowing up-and-down movement.
- Feet: Support the body and enable walking, made up of numerous bones, joints, and muscles, including the arch, heel, and toes.
Functions of Human Body Parts
Head and Neck
The head and neck region is a complex structure that houses the brain, responsible for controlling all bodily functions, thoughts, and emotions. The eyes enable vision, the ears facilitate hearing and balance, the nose is involved in smell and breathing, the mouth aids in eating, tasting, speaking, and breathing, and the throat is essential for swallowing, breathing, and voice production. The neck supports the head and allows its movement, containing vital structures like the cervical spine and thyroid gland.
Upper Body
The upper body consists of the shoulders, which allow arm movement and provide stability, and the arms, enabling various movements like lifting and carrying. The hands facilitate grasping, touching, and fine motor skills, while the chest protects vital organs like the heart, responsible for pumping blood, and the lungs, which enable breathing and oxygen exchange. The back supports the body and protects the spinal cord, a crucial part of the nervous system.
Midsection
The midsection is home to vital digestive and metabolic organs. The stomach breaks down food using enzymes and acids, the liver metabolizes nutrients and detoxifies substances, and the kidneys filter blood and regulate electrolytes. The intestines are responsible for nutrient absorption and waste elimination, the pancreas produces digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin, the spleen supports the immune system, and the gallbladder stores bile, aiding in fat digestion.
Lower Body
The lower body provides support and mobility. The hips are ball-and-socket joints that connect the legs to the torso, allowing movement in multiple directions. The thighs contain muscles that enable walking, running, and jumping, while the knees allow bending and straightening of the legs. The legs, including the shins and calves, support weight and enable movement, and the ankles and feet provide stability, support body weight, and maintain balance.
Name of Body Parts (External) in Hindi
Name of boyd parts in Hindi is given in the following table below. The table is divided into four columns: the English name, the Hindi script, the transliteration of the Hindi name, and a general category for the body part.
| English | Hindi Script | Transliteration | Body Part Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Head | सिर | Sir | Head |
| Hair | बाल | Baal | Head |
| Eye | आंख | Aankh | Face |
| Ear | कान | Kaan | Face |
| Nose | नाक | Naak | Face |
| Mouth | मुंह | Muh | Face |
| Teeth | दांत | Daant | Face |
| Tongue | जीभ | Jeebh | Face |
| Neck | गरदन | Gardan | Neck & Shoulders |
| Shoulder | कंधा | Kandha | Neck & Shoulders |
| Arm | बाजू | Baazu | Limbs |
| Hand | हाथ | Haath | Limbs |
| Fingers | उंगलियाँ | Ungliyan | Limbs |
| Chest | छाती | Chhaati | Torso |
| Stomach | पेट | Pet | Torso |
| Back | पीठ | Peeth | Torso |
| Leg | टांग | Taang | Limbs |
| Knee | घुटना | Ghutna | Limbs |
| Foot | पैर | Pair | Limbs |
| Skin | त्वचा | Tvacha | General |
| Thigh | जांघ | Jangh | Limbs |
| Elbow | कोहनी | Kohni | Limbs |
| Wrist | कलाई | Kalai | Limbs |
| Ankle | टखना | Takhna | Limbs |
| Forehead | माथा | Maatha | Face |
| Eyebrow | भौंह | Bhaunh | Face |
| Lip | होंठ | Honth | Face |
| Chin | ठोड़ी | Thodi | Face |
| Waist | कमर | Kamar | Torso |
| Hip | नितंब | Nitamb | Torso |
Name of Internal Body Parts in Hindi
This table includes various internal organs and systems, such as the heart, brain, lungs, liver, kidneys, and more, along with their corresponding Hindi script and transliteration.
| English | Hindi Script | Transliteration |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | दिल | Dil |
| Brain | मस्तिष्क | Mastishk |
| Lung | फेफड़ा | Fefda |
| Liver | जिगर | Jigar |
| Kidney | गुर्दा | Gurda |
| Stomach (Organ) | अमाशय | Amashay |
| Intestine | आंत | Aant |
| Pancreas | अग्नाशय | Agnashay |
| Spleen | प्लीहा | Pliha |
| Gallbladder | पित्ताशय | Pittashay |
| Esophagus | ग्रासनली | Grasanali |
| Bladder | मूत्राशय | Mootrashay |
| Blood Vessels | रक्त वाहिकाएं | Rakt Vahikaen |
| Spinal Cord | रीढ़ की हड्डी | Reedh Ki Haddi |
| Bones | हड्डियाँ | Haddiyan |
| Muscles | मांसपेशियां | Maanspeshiyan |
Conclusion
The human body is a marvel of nature, with each part playing a unique role in maintaining overall health and function. Understanding the names and functions of body parts is not only fascinating but also essential for recognizing how the body works. Whether for medical understanding or general education, this knowledge empowers us to appreciate the complexity and beauty of the human form.
FAQs: Name of Human Body Parts
- What are the main parts of the human body?
- The main parts include the head, neck, upper body (arms, chest, back), midsection (abdominal organs), and lower body (legs, feet).
- How many bones are in the human body?
- The adult human body typically has 206 bones.
- What are the largest and smallest organs in the body?
- The skin is the largest organ, while the pineal gland is one of the smallest.
- How do the body parts work together?
- Body parts work together through a complex system of coordination, controlled by the nervous system, to perform various functions.
- Why is it important to know the names of body parts?
- Knowing the names of body parts helps in understanding human anatomy, communicating medical conditions, and promoting health awareness.
The exploration of the human body and its parts is a journey into the intricacies of biology and physiology. It’s a reminder of the delicate balance and harmony that sustains life. Whether you’re a student, a medical professional, or simply curious, understanding the names of body parts opens the door to a deeper appreciation of the human experience.
